The Challenge
A customer approached us with a straightforward request:
They wanted users to dial a phone number and have a natural conversation with an AI agent that could recommend restaurants, answer menu and opening-hours questions, and initiate reservations or delivery orders.
The technical reality was less trivial.
Voice interactions are unforgiving. Even small delays break conversational flow, and stitching together multiple speech and AI services often introduces latency, complexity, and brittle integrations.
The key challenges were:
- Natural, real-time conversations with minimal end-to-end latency
- Dynamic restaurant recommendations based on user preferences mid-call
- Multi-turn context handling, including follow-up questions on specific venues
- Telephony integration with existing phone infrastructure
- Scalability, supporting multiple concurrent inbound calls without manual intervention
This POC needed to prove that a speech-to-speech AI agent could feel fluid, responsive, and production-viable, without overengineering the stack.
What The Customer Needed
- Low-latency voice AI that didn’t feel robotic or laggy
- Simplified architecture without chaining multiple speech and LLM services
- Fast iteration to validate conversational flows before production investment
- Cloud-native scalability with minimal operational overhead
- Clear production path, even if the first phase was experimental
The Solution: Azure Voice Live API with Call Center Accelerator
The solution was built using the Azure Call Center Voice Agent Accelerator, powered by the Azure Voice Live API.
Instead of orchestrating separate ASR, LLM, and TTS services, the Voice Live API provided a single, unified speech-to-speech endpoint, significantly reducing latency and architectural complexity.
The POC focused on validating conversational quality, system responsiveness, and operational feasibility under real phone-call conditions.
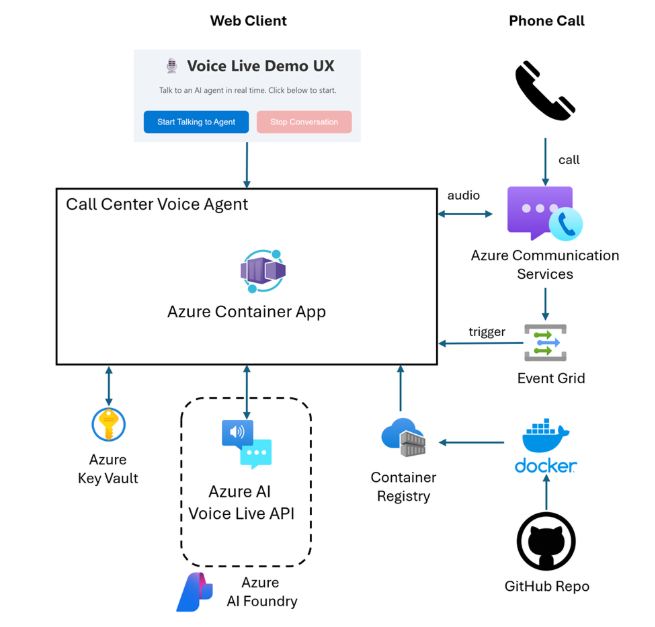
Architecture Overview
The solution consists of three main components:
- Azure Communication Services (ACS) – Handles telephony integration and call routing
- Azure Voice Live API – Provides the speech-to-speech engine combining ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition), LLM, and TTS (Text-to-Speech) in a unified interface
- Backend Service – Orchestrates the conversation flow and business logic, deployed on Azure Container Apps
When a user calls the service number, ACS routes the call to our backend service, which establishes a connection with the Voice Live API. The API handles the entire speech-to-speech pipeline, eliminating the need to manually chain together separate speech recognition, language model, and synthesis services.
Key Technical Decisions
Why Voice Live API?
Traditional voice agent implementations require orchestrating multiple services: speech-to-text for transcription, a language model for understanding and generation, and text-to-speech for responses. The Voice Live API consolidates these into a single endpoint with optimized latency, which was critical for maintaining natural conversation flow.
Deployment Strategy
We used Azure Developer CLI (azd) for infrastructure provisioning and deployment. This provided:
- Consistent deployment across environments
- Infrastructure-as-code through Bicep templates
- Simplified resource management and teardown
The backend service runs as a containerized application on Azure Container Apps, providing automatic scaling and simplified management.
Testing Approach
The accelerator provides two client interfaces:
- A web-based client for rapid testing during development using browser microphone/speaker
- The ACS phone client for end-to-end testing with actual phone calls
This dual approach allowed us to iterate quickly during development while ensuring production-like testing before deployment.
Implementation Details
Conversation Flow
The agent follows this interaction pattern:
- Initial Greeting – Agent introduces itself and asks about food preferences
- Preference Collection – User describes cuisine type or specific preferences
- Restaurant Recommendations – Agent provides a curated list of options
- Detail Inquiries – User can ask about specific restaurants (menu, hours, location)
- Action Completion – User can request table reservation or food delivery
The LLM backing the Voice Live API handles context management across this multi-turn conversation, maintaining awareness of previously mentioned restaurants and user preferences.
Configuration and Customization
The accelerator is designed for flexibility. Key configuration points include:
- System prompts to define agent personality and behavior
- Speech recognition settings for language and accuracy tuning
- TTS voice selection from Azure’s neural voice library
- Turn-taking behavior to control when the agent stops listening
For this restaurant use case, we customized the system prompt to include domain knowledge about restaurant types, common questions, and appropriate response formats.
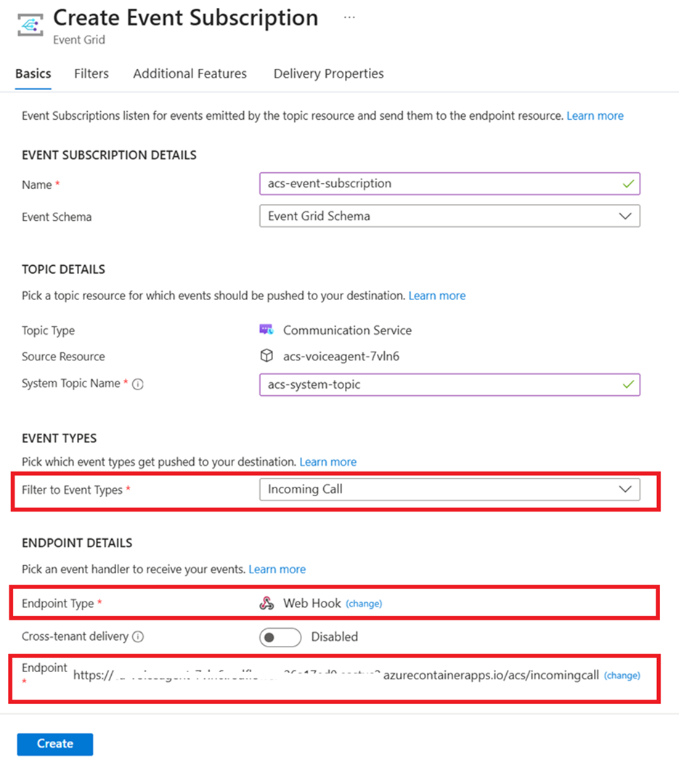
Event Grid Integration
To receive incoming calls, we configured an Azure Event Grid subscription:
- Event Type: IncomingCall
This webhook triggers when someone dials the ACS phone number, initiating the voice agent session.
Deployment Process
The deployment was streamlined through the accelerator template:
# Initialize the project
azd init -t Azure-Samples/call-center-voice-agent-accelerator
# Authenticate to Azure
azd auth login
# Deploy all resources
azd up
The azd up command provisions:
- Azure AI Speech Services with Voice Live API access
- Azure Communication Services with phone number
- Azure Container Apps for hosting the service
- Azure Container Registry for image storage
- Necessary networking and IAM configurations
We selected swedencentral as the deployment region due to Azure AI Foundry availability requirements.
Business Outcomes
The POC delivered clear, measurable business value beyond technical validation:
- Faster Time-to-Validation
The accelerator-based approach allowed the customer to move from concept to live phone-based testing in days, not weeks, significantly reducing experimentation costs.
- Lower Engineering Overhead
By avoiding custom orchestration of multiple speech and AI services, the team minimized glue code, reduced failure points, and simplified long-term maintenance.
- Improved Customer Experience Potential
Sub-2-second response times enabled natural, interruption-free conversations critical for user adoption in voice-driven services.
- Predictable Scaling Model
Usage-based pricing and serverless container scaling provided a clear cost-to-call model, making it easier to forecast production costs tied directly to call volume.
- Clear Path to Production
The architecture established a solid foundation for future expansion, including analytics, state persistence, and escalation to human agents, without requiring a redesign.
Production Considerations
To move beyond POC, we identified several next steps:
- Persistent conversation state across calls
- Analytics and monitoring for intent tracking and agent performance
- Fallback mechanisms for misunderstood requests
- Load testing for peak call volumes
- Regional rollout planning based on service availability
Why It Matters
This case shows that high-quality voice AI experiences don’t require complex, fragile architectures.
Leveraging Azure’s speech-to-speech capabilities and cloud-native services proved it’s possible to deliver natural, scalable voice interactions while keeping engineering effort and operational risk under control.
The result: a validated, production-ready direction for voice-based customer engagement, grounded in real-world performance.